According to the Centers for Disease Control and the National Heart, atrial fibrillation icd 10 is the most common arrhythmia type. It creates the heartbeat significantly faster than usual. As a result, the upper and lower cells of the heart can not work together. It can be fatal and even life-threatening if left untreated. All over the world, this is the most common faced cardiac disease. It affects 2% of the general people and rises to 10% of those 80 up aged people.
It is the most common disease in the critical care environment. However, it causes by the heart’s electrical system problems. A study of the American Heart Association said that about 2.7 million Americans live with AF. To ensure due payout, critical care experts should know about these new and existing codes. Still, their definitions and ensure documentation that gleams the professional services that support the codes. Critical consideration medical billing and coding services are obtainable to help with this.
There are four kinds of afib. They are paroxysmal, persistent, long-standing persistent, and permanent. The ICD-10-CM codes situation for each type of afib is shown in the Table. In 2020, The ICD-10-CM added some new codes for chronic, permanent, persistent, and long-standing permanent afib, all of that are CCs. We will describe all about atrial fibrillation in today’s article. So follow this article from top to bottom.
Table of Contents
What is atrial fibrillation icd 10
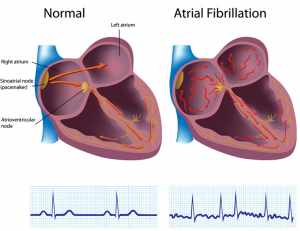
Atrial fibrillation icd 10 is one kind of irregular heartbeat; it also can say quivering heart. However, it can cause to develop blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and so many. It often leads to an increase in heart rate and impairs blood flow.
When a person is infected with this disease, the heartbeat’s upper chambers are different from the lower chambers; when these fitful heartbeats happen, it relaxes and fills the wrong and empties the ventricles. It often refers to chaotic Diseases.
The reason for this disease is strange, but it is liable for the damage to the heart’s electrical system.
It can develop in any person with children, but the risk is higher in high-age patients. Still, the person who has a family history, diabetes and asthma are in this disease’s danger zone.
It is essential to treat this disease like an erratic heartbeat. Proper treatment often makes this diesis go away. If this does not help the insecure span, the patient may need to be treated with beta-blockers.
The calcium channel blockers help slow the heart rate. The span should be restored to a regular beat to decrease the intense heart rate. Patients are often positioned on a blood thinner to help prevent blood clots and stroke and the rate and rhythm controller medication. Victims often keep the blood thinner to help prevent blood clots. Still, stroke may cause in addition to the rate and beat controller pill. There are many other treatments for atrial fibrillation icd 10. Which procedure does not correct on its own or does not respond to the medications.
Atrial Fibrillation 10– What is it, and how do you code it
Only one code has been found for many years to report this condition. The doctor even named what kind of patient he was. There are four codes for reporting atrial fibrillation icd 10:
I48.91 Use to report if no other term is ready.
I48.2 Use to report if specified as chronic or stable
I48.0 use to report when named as paroxysmal.
I48.0 Use to report when named as constant.
How to code multiple documented types of atrial fibrillation
The most recent coding advice has aimed at how to report the proper code for atrial fibrillation icd 10 when more than one type is the record. Per this advice, if the doctor solution the patient with the chronic patient, only the code I48.1 is listed. The term chronic is a specific term that could also define the other types of named Diseases. Since I48.1 is a more specific code, it should be reported even though the Alphabetic Index within ICD-10-CM has listed the different diseases. At the same sign level, only one code should report. The most particular term needs to be reported.
Atrial Fibrillation Coding Tips
- It is still listing in patients that are not currently seeing the erratic beat. As long as the patient is asking open-ended remedies to help control this rate.
- It is very common in patients and should be verified as complex before coding.
- When multiple types of disease records in record, select the most specific type.
Diagnosis Code I48.9
Unspecified atrial fibrillation icd 10
- 91 is a specific ICD-10-CM code that can use to show a judgment for payment purposes.
- The 2021 version of ICD-10-CM I48.91 became valid on October 1, 2020.
- It is the American ICD-10-CM story of I48.91 – other global reports of ICD-10 I48.91 may change.
The later code above I48.91 contains notes back-books.
that may be fit to I48.91:
I00-I99
- Diseases of the circulatory system
Close Synonyms
- Atrial fibrillation
- with a fast ventricular reply
ICD-10-CM I48.91 filed in Diagnostic Related Group (MS-DRG v38.0):
- 308 This conduction hits with MCC
- 309 arrhythmia and this disorders with cc
- 310 Cardiac and other strikes out cc/MCC
- 791 Prematurity with main problems
- 793 Full term neonate with main problems
Convert I48.91 to ICD-9-CM
Code History
- 2016 (active 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM)
- 2017 (effective 10/1/2016): No change
- 2018 (active 10/1/2017): Not change
- 2019 (effective 10/1/2018): No change
- 2020 (active 10/1/2019): Not change
- 2021 (effective 10/1/2020): No change
Analysis Index notes including back-references to I48.91:
- Fibrillation
- atrial or auricular (built) I48.91
Payment claims with a date of help on or after October 1, 2015, require the Use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Symptoms
AF can exist without any signs and remain furtive until the person has a medical check-up. The common signs of this diseases are:
- First of all, Beats– fast irregular pulse, beating, shaking, or flip-flops in the chest
- Then, Dizziness
- Brevity of breath
- After that Fatigue
- Feel Weak
- Then Reduced energy to apply
- Lastly Lightheadedness
- Heart pain
AF can cause blood masses, stroke, hypotension, and heart bust with organ dysfunction.
Causes
The correct causes of these diseases are unknown. But it is usually held the result of high blood force and coronary artery disease. Conditions that raise the risk of developing AF include:
- Age
- Then Heart attack and forms– Heart attack, coronary vein problem, unusual heart valves, natural heart defects
- Family story
- Rest apnea
- However, Thyroid problem
- Diabetes
- Fever
- After that, Fixed kidney problem
- Prior heart operation
- And, Viral germs
- Tension due to operation, disease, or other attacks
- Danger to drugs, such as pills, caffeine, smoke or drink
- Sick sinus sign
- Finally, taking alcohol
Since there are many kinds of problems, trials using an ECG, Holter director, event recorder may be required to allow correct analysis. Indicating AF type will help proper treatment plan.
Codes to report Atrial Fibrillation icd 10
In 2019, there were four codes on the report atrial fibrillation icd 10:
- 0 about AF
- 1 Resolute
- 2 permanent
- 91 General
On October 1, 2020, class I48 was grown, with more limited options for persistent and permanent problems as follows:
- I48 problem and flutter
- 0 around this problem
- 1 Resolute atrial fibrillation
- 11 Permenant resolute of problem
- 19 Other resolute problem and daisies
- Permanent persistent
- The persistent problem of NOS
- 2 Permanent problem and others
- 20 Chronic illness, general
- 21 Permanent general diseases
- 91 General problem
- 92 leg pain
New AF Code Definitions
- Too, knowing the keys for the new AF codes is vital to use them rightly:
- The general irregular fibrillation comes and goes but never serves longer than a week and solves on its own without treatment.
- Persistent serves longer than a week and less than a year; needs a proper way to turn the heart to a regular beat and repeat the treatment when the health returns.
- Long time suffering people who last richer than a year and always need repeat electrical support.
- Other resolute regularly listed as “chronic resolute” Other vital things that last longer than a week, but not more than a year; needs regular treatment.
- Chronic general things vague– lasts longer than a year and is non-hard, meaning it won’t answer the line and has not yet named the medical record as vital.
- Permanent diseases have lasted longer than a year and are not a response to cardioversion. However, this for these cases is no longer meant, cannot be done, or will not be completed.
- The general cause came when the document does not know the specific types.
Coding AF – Key Considerations
In 2020, ICD-10 added new codes for fixed, strong, committed, and long-standing permanent AF, all of which are CCs. In an inpatient setting, to determine disease needs to report as a certain diagnosis. A Nov 2019 ACP Hospitalist article presents key points about using the new ICD-10 codes for AF.
- “Chronic AF” is a nonspecific term that means that AF of any type has lasted more than three months and could add permanent, persistent, or long-lasting persistent AF. This report uses the code I48.20 when the special type of AF is not documented.
● When the analysis is atrial flutter, select both of the codes for (I48.92), and it depends on the special type of matter.
- Then the correct CC status of each named AF type must be won. For this, the documentation should show the special type of AF and should never be left general as “AF” (code I48.91, a non-CC).
- AF strongly controlled by hard ablation only(not asking for any medicine) should report using code Z86.79.
- If a cardiac problem for AF actors and the case still needs medicine to stop rotation, the analysis should be AF and not “history of AF.”
- The history of AF (code Z86.79) should use only when the verb AF has been changed to sinus beat and needs no open-ended way to prevent the return or when remove cure alone has used to control AF.
However, the codes selected should help medical needs. Test reports may give details about an analysis not held in the ordering provider’s record. In this case, a higher unique code to help that analysis can come only if the system doctor studied the test’s effects and said that he accepts the findings.
Partnering with an able important care coding and medical service provider is a useful option to ensure correct reports using the latest codes.
Essential Coding Information of atrial fibrillation icd 10
In the office or other outdoor setting, an estimate that times, Rule out in this patient with long brevity of pants and beats. It will tell the prefix rather than the analysis codes listed above since the diagnosis has not yet been proved. However, in a patient setting, it would be due to reporting persistence. It is a confirmed diagnosis because there are many rules for telling likely reports for inpatients.
Selecting the correct code to support medical needs is also great. For example, a stable illness wouldn’t help the medical need for a major problem. Sinch, by meaning, problems has not and will not fix. So the system would be vain for this patient. Asking the provider for an explanation is probably necessary.
Often reports from outer testing plants will provide details of diagnoses not held by the ordering provider. In contrast, it may be attractive to use those details from the outer report in the code choice for higher specificity. That might go upon the rules of coding. There is, however, a situation that might allow the coder to code rightly from the test report. Suppose the booking provider analyzed the results of the test and said that he agreed with the findings. It would be proper to include those details to report a higher certain code.
Conclusive Discussion of atrial fibrillation icd 10
Above all, we can hope that now you know all about atrial fibrillation icd 10. We tried and researched a lot to explain the whole thing simply and easily. If you have any questions, then feel free to knock us by the comment box. We will try to appreciate your queries.